This site is intended for healthcare professionals practicing in the US.
©2022 AstraZeneca. All rights reserved.
US-69609
Last Updated 11/22
The information provided on this site is intended for use by healthcare professionals practicing in the US. The dissemination of this information may be subject to different medical and regulatory requirements in other countries.
This web site is intended to help healthcare professionals practicing in the US and AstraZeneca authorized persons find scientifically balanced, evidence-based information about AstraZeneca drugs, submit a question, ask for field medical follow-up, and explore links to professional and patient support resources.
Are you a healthcare professional practicing in the United States?
Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA)
AstraZeneca Medical's ambition is to address unmet needs for people living with inflammatory diseases driven by eosinophilic inflammation.
Watch Eosinophils in Action in EGPA
What is EGPA?
EGPA is a complex, rare, multisystem disease characterized by necrotizing vasculitis and eosinophilic inflammation, which is associated with adult-onset asthma and nasal polyps.1-3 The US incidence rate is estimated at 1 to 3 cases per 100,000 adults per year.4
EGPA is the rarest subgroup among the AAVs, although the majority of patients with EGPA are ANCA negative.1,2
What are Eosinophils?
Eosinophils contribute to inflammation both directly and indirectly3
Direct Mechanisms of Inflammation
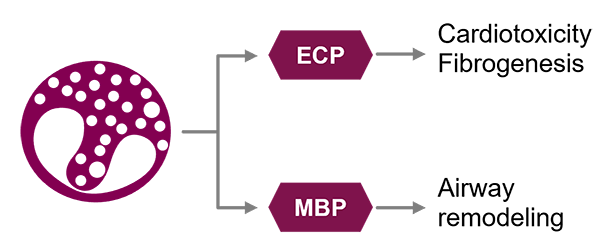
Cytotoxicity and Microenvironment Manipulation
Indirect Mechanisms of Inflammation
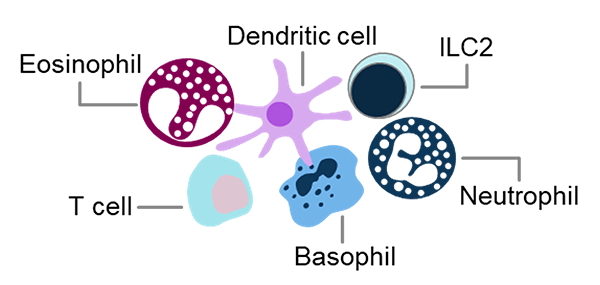
Chronic Inflammation

Ischemic Damage
Eosinophils Are Involved in All Phases of EGPA
Spectrum of Clinical Manifestations of EGPA
Although EGPA has historically been segregated into 2 distinct phenotypes based on the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms, it may present as a spectrum of disease phenotypes with overlapping pathological mechanisms that cannot be defined by a single serological or clinical parameter.7,11
Abbreviations
AAV = antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis
;ANCA = antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
;ECP = eosinophilic cationic protein
;EDN = eosinophil-derived neurotoxin
;EGPA = eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
;ENT = ear, nose, and throat
;EPO = eosinophil peroxidase
;GI = gastrointestinal
;GPA = granulomatosis with polyangiitis
;ILC2 = type 2 innate lymphoid cell(s)
;MBP = major basic protein
;MPA = microscopic polyangiitis
;US = United States
References
1. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(1):1-11. doi:10.1002/art.37715
2. Furuta S, Iwamoto T, Nakajima H. Update on eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Allergol Int. 2019;68(4):430-436. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2019.06.004
3. Khoury P, Grayson PC, Klion AD. Eosinophils in vasculitis: characteristics and roles in pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(8):474-483. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2014.98
4. Vasculitis Foundation. Pediatric vasculitis. Who gets EGPA? Vasculitis Foundation website. https://www.vasculitisfoundation.org/pediatrics-vasculitis/pediatric-types/pediatric-eosinophilic-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis/
5. Yates M, Watts R. ANCA-associated vasculitis. Clin Med (Lond). 2017;17(1):60-64. doi:10.7861/clinmedicine.17-1-60
6. Chung SA, Seo P. Microscopic polyangiitis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2010;36(3):545-558. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2010.04.003
7. Trivioli G, Terrier B, Vaglio A. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: understanding the disease and its management. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(suppl 3):iii84-iii94. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez570
8. Ramirez GA, Yacoub MR, Ripa M, et al. Eosinophils from physiology to disease: a comprehensive review. BioMed Res Int. 2018;2018:9095275. doi:10.1155/2018/9095275
9. Rosenberg HF, Dyer KD, Foster PS. Eosinophils: changing perspectives in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(1):9-22. doi:10.1038/nri3341
10. Jacobsen EA, Jackson DJ, Heffler E, et al. Eosinophilic knockout humans: uncovering the role of eosinophils through eosinophil-directed biologic therapies. Annu Rev Immunol. 2021;39:719-757. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-093019-125918
11. Fagni F, Bello F, Emmi G. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: dissecting the pathophysiology. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:627776. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.627776
12. Koike H, Nishi R, Furukawa S, et al. In vivo visualization of eosinophil secretion in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: an ultrastructural study. Allergol Int. 2022;71(3):373-382. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2022.02.009
13. Chakraborty RK, Aeddula NR. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome). In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; March 23, 2023.
14. Gioffredi A, Maritati F, Oliva E, et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: an overview. Front Immunol. 2014;5:549. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00549
US-88106, US-91275 Last Updated 7/24